Improper dihedrals are a measure of the chirality/planarity of the structure at a specific atom. Values around -35 or +35 are expected for chiral atoms, and values around 0 for planar atoms. Planar side chains are left out of the calculations, these are better handled by the planarity checks.
Three numbers are given for each atom in the table. The first is the Z-score for the improper dihedral. The second number is the measured improper dihedral. The third number is the expected value for this atom type. A final column contains an extra warning if the chirality for an atom is opposite to the expected value.
83 VAL ( 113 ) C -4.3 -9.0 -0.2
Improper dihedral RMS Z-score : 0.661
Note: Chain names are OK
All chain names assigned to polymer molecules are unique, and all
residue numbers are strictly increasing within each chain.
Note: Weights checked OK
All atomic occupancy factors ('weights') fall in the 0.0--1.0 range.
Geometric checks
Note: No missing atoms detected
All expected atoms are present.
Warning: C-terminal oxygen atoms missing
The C-atoms listed in the table below belong to a C-terminal residue
in a protein chain, but the C-terminal oxygen ("O2" or "OXT") that it
should be bound to was not found.
92 SER ( 122 ) C
RMS Z-score for bond lengths: 0.711
RMS-deviation in bond distances: 0.016
Note: No bond length directionality
Comparison of bond distances with Engh and Huber [REF] standard
values for protein residues and Parkinson et al [REF] values for
DNA/RNA does not show significant systematic deviations.
Warning: Unusual bond angles
The bond angles listed in the table below were found to deviate
more than 4 sigma from standard bond angles (both standard values
and sigma for protein residues have been taken from Engh and Huber
[REF], for DNA/RNA from Parkinson et al [REF]). In the table below
for each strange angle the bond angle and the number of standard
deviations it differs from the standard values is given. Please
note that disulphide bridges are neglected. Atoms starting with "<"
belong to the previous residue in the sequence.
84 LEU ( 114 ) C CA CB 118.877 4.6
RMS Z-score for bond angles: 0.910
RMS-deviation in bond angles: 1.791
Note: Side chain planarity OK
All of the side chains of residues that have a planar group are
planar within expected RMS deviations.
Note: Atoms connected to aromatic rings OK
All of the atoms that are connected to planar aromatic rings in side
chains of amino-acid residues are in the plane within expected RMS
deviations.
Note: No prolines in structure
Since there are no proline residues in the structure, the PRO puckering
check was skipped.
Note: Torsion angles OK
All individual residues have normal overall torsion angle scores.
Warning: Backbone torsion angle evaluation shows unusual conformations
The residues listed in the table below have abnormal backbone torsion
angles.
Residues with ``forbidden'' phi-psi combinations are listed, as well as residues with unusual omega angles (deviating by more than 3 sigma from the normal value). Please note that it is normal if about 5 percent of the residues is listed here as having unusual phi-psi combinations.
36 MET ( 65 ) Poor phi/psi
Ramachandran Z-score : -2.268
Warning: Omega angles too tightly restrained
The omega angles for trans-peptide bonds in a structure are
expected to give a gaussian distribution with the average around
+178 degrees and a standard deviation around 5.5 degrees. These
expected values were obtained from very accurately determined
structures. Many protein structures are too tightly constrained.
This seems to be the case with the current structure, as the
observed standard deviation is below 4.0 degrees.
Standard deviation of omega values : 2.663
Note: chi-1/chi-2 angle correlation Z-score OK
The score expressing how well the chi-1/chi-2 angles of all residues
are corresponding to the populated areas in the database is
within expected ranges for well-refined structures.
chi-1/chi-2 correlation Z-score : 0.610
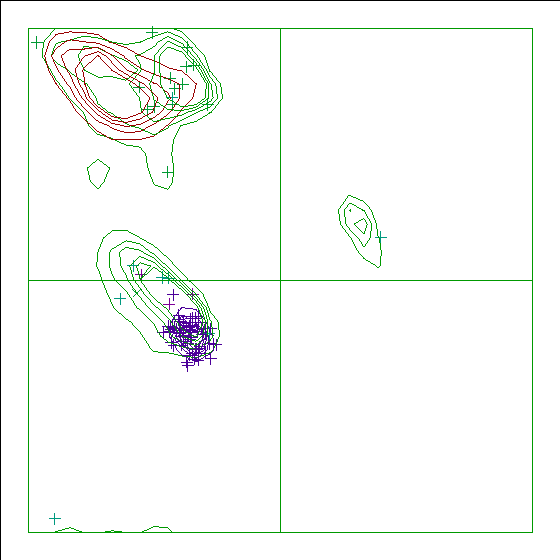
Note: Ramachandran plot
In this Ramachandran plot X-signs represent glycines, squares represent
prolines and small plus-signs represent the other residues. If too many
plus-signs fall outside the contoured areas then the molecule is poorly
refined (or worse).
In a colour picture, the residues that are part of a helix are shown in blue, strand residues in red. "Allowed" regions for helical residues are drawn in blue, for strand residues in red, and for all other residues in green.

Chain without chain identifier
Accessibility related checks
Warning: Inside/Outside residue distribution unusual
The distribution of residue types over the inside and the outside of the
protein is unusual. Normal values for the RMS Z-score below are between
0.84 and 1.16. The fact that it is higher in this structure could be
caused by transmembrane helices, by the fact that it is part of a
multimeric active unit, or by mistraced segments in the density.
inside/outside RMS Z-score : 1.217
Note: Inside/Outside RMS Z-score plot
The Inside/Outside distribution normality RMS Z-score over a 15
residue window is plotted as function of the residue number. High
areas in the plot (above 1.5) indicate unusual inside/outside
patterns.
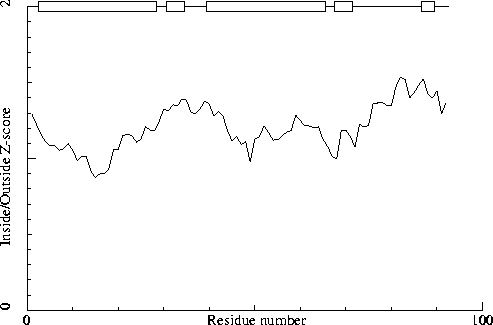
Chain without chain identifier
Secondary structure
Note: Secondary structure
This is the secondary structure according to DSSP. Only helix (H), strand
(S), turn (T) and coil (blank) are shown. [REF]
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
10 20
| |
1 - 29 LDDHDDEDLQSGLTALVVTVVELLVEALE
1 - 29 HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
30 40 50 60
| | | |
30 - 66 GEAVRRMESGSLSDAEIERLGSQLQALEAELDRLQAD
30 - 66 HHHHTT HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
70 80 90
| | |
67 - 92 QDIEAAVDEFKDDLDHVLRDAITQMS
67 - 92 HHHHT TTT TT333
The contact distances of all atom pairs have been checked. Two atoms are said to `bump' if they are closer than the sum of their Van der Waals radii minus 0.40 Angstrom. For hydrogen bonded pairs a tolerance of 0.55 Angstrom is used. The first number in the table tells you how much shorter that specific contact is than the acceptable limit. The second distance is the distance between the centers of the two atoms.
The last text-item on each line represents the status of the atom pair. The text `INTRA' means that the bump is between atoms that are explicitly listed in the PDB file. `INTER' means it is an inter-symmetry bump. If the final column contains the text 'HB', the bump criterium was relaxed because there could be a hydrogen bond. Similarly relaxed criteria are used for 1--3 and 1--4 interactions (listed as 'B2' and 'B3', respectively). If the last column is 'BF', the sum of the B-factors of the atoms is higher than 80, which makes the appearance of the bump somewhat less severe because the atoms probably aren't there anyway.
Bumps between atoms for which the sum of their occupancies is lower than one are not reported. In any case, each bump is listed in only one direction.
84 LEU ( 114 ) CB -- 89 THR ( 119 ) CB 0.984 2.216 INTRA 83 VAL ( 113 ) O -- 84 LEU ( 114 ) CG 0.635 2.165 INTRA 84 LEU ( 114 ) CG -- 89 THR ( 119 ) CB 0.449 2.751 INTRA 84 LEU ( 114 ) CB -- 89 THR ( 119 ) CG2 0.443 2.757 INTRA 84 LEU ( 114 ) CB -- 89 THR ( 119 ) OG1 0.428 2.372 INTRA 19 THR ( 43 ) CG2 -- 56 LEU ( 85 ) CD1 0.305 2.895 INTRA 84 LEU ( 114 ) CD2 -- 89 THR ( 119 ) CG2 0.292 2.908 INTRA 84 LEU ( 114 ) CD1 -- 89 THR ( 119 ) CB 0.237 2.963 INTRA 83 VAL ( 113 ) C -- 84 LEU ( 114 ) CG 0.186 3.014 INTRA 19 THR ( 43 ) C -- 56 LEU ( 85 ) CD1 0.125 3.075 INTRA 82 HIS ( 112 ) CE1 -- 91 MET ( 121 ) CG 0.125 3.075 INTRA 83 VAL ( 113 ) O -- 84 LEU ( 114 ) CB 0.111 2.689 INTRA 16 LEU ( 40 ) CD1 -- 56 LEU ( 85 ) CD2 0.107 3.093 INTRA 3 ASP ( 27 ) O -- 7 GLU ( 31 ) CG 0.106 2.694 INTRA 23 LEU ( 47 ) CD1 -- 56 LEU ( 85 ) CD1 0.105 3.095 INTRA 84 LEU ( 114 ) CD2 -- 89 THR ( 119 ) CB 0.098 3.102 INTRA 20 VAL ( 44 ) N -- 56 LEU ( 85 ) CD1 0.097 3.003 INTRA 1 LEU ( 25 ) CD1 -- 3 ASP ( 27 ) OD1 0.074 2.726 INTRA 82 HIS ( 112 ) CE1 -- 91 MET ( 121 ) CB 0.068 3.132 INTRA 39 GLY ( 68 ) O -- 40 SER ( 69 ) C 0.057 2.743 INTRA BF 81 ASP ( 111 ) OD1 -- 82 HIS ( 112 ) O 0.043 2.357 INTRA 2 ASP ( 26 ) OD2 -- 5 ASP ( 29 ) OD2 0.041 2.209 INTRA HB 13 LEU ( 37 ) CD1 -- 63 LEU ( 92 ) CB 0.039 3.161 INTRA 50 GLY ( 79 ) O -- 54 GLN ( 83 ) NE2 0.031 2.519 INTRA HB 23 LEU ( 47 ) O -- 24 LEU ( 48 ) C 0.017 2.783 INTRA 28 LEU ( 52 ) O -- 29 GLU ( 53 ) C 0.015 2.785 INTRA 68 ASP ( 98 ) O -- 69 ILE ( 99 ) C 0.013 2.787 INTRA 18 VAL ( 42 ) O -- 19 THR ( 43 ) C 0.010 2.790 INTRA 4 HIS ( 28 ) O -- 5 ASP ( 29 ) C 0.005 2.795 INTRA BF 35 ARG ( 64 ) N -- 36 MET ( 65 ) N 0.004 2.596 INTRA BF
The packing environment of the residues is compared with the average packing environment for all residues of the same type in good PDB files. A low packing score can indicate one of several things: Poor packing, misthreading of the sequence through the density, crystal contacts, contacts with a co-factor, or the residue is part of the active site. It is not uncommon to see a few of these, but in any case this requires further inspection of the residue.
85 ARG ( 115 ) -7.51 91 MET ( 121 ) -6.99 83 VAL ( 113 ) -5.23
Average for range 1 - 92 : -0.563
Note: Quality value plot
The quality value smoothed over a 10 residue window is plotted as
function of the residue number. Low areas in the plot (below
-2.0) indicate "unusual" packing.
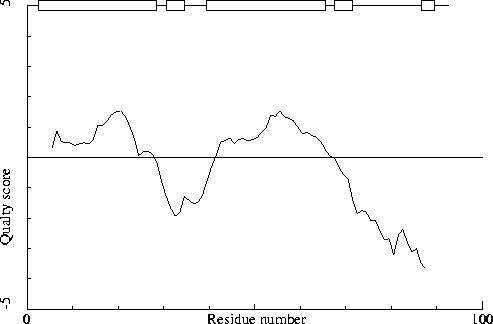
Chain without chain identifier
Warning: Low packing Z-score for some residues
The residues listed in the table below have an unusual packing
environment according to the 2nd generation quality check. The score
listed in the table is a packing normality Z-score: positive means
better than average, negative means worse than average. Only residues
scoring less than -2.50 are listed here. These are the "unusual"
residues in the structure, so it will be interesting to take a
special look at them.
88 ILE ( 118 ) -3.67 76 PHE ( 106 ) -3.32 84 LEU ( 114 ) -2.66
All contacts : Average = 0.369 Z-score = 2.59
BB-BB contacts : Average = 0.731 Z-score = 5.24
BB-SC contacts : Average = -0.054 Z-score = -0.20
SC-BB contacts : Average = 0.467 Z-score = 3.01
SC-SC contacts : Average = -0.286 Z-score = -1.26
Note: Second generation quality Z-score plot
The second generation quality Z-score smoothed over a 10 residue window
is plotted as function of the residue number. Low areas in the plot (below
-1.3) indicate "unusual" packing.
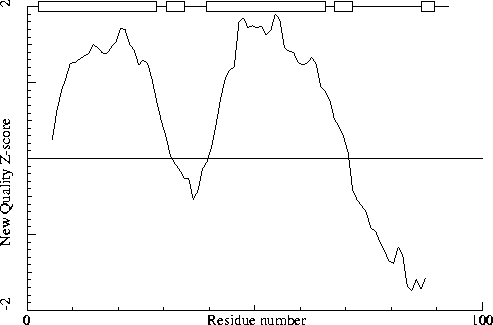
Chain without chain identifier
Note: Backbone oxygen evaluation OK
All residues for which the local backbone conformation could be
found in the WHAT IF database have a normal backbone oxygen
position.
Note: Rotamers checked OK
None of the residues that have a normal backbone environment have
abnormal rotamers.
Note: Backbone conformations OK
None of the residues have abnormal backbone conformations
Note: Backbone conformation Z-score OK
The backbone conformation analysis gives a score that is normal
for well refined protein structures.
Backbone conformation Z-score : 1.501
B-factor analysis
Warning: Average B-factor problem
The average B-factor for all buried protein atoms normally lies between
10--20. Values around 3--5 are expected for X-ray studies performed
at liquid nitrogen temperature.
Because of the extreme value for the average B-factor, no further analysis of the B-factors is performed.
Average B-factor for buried atoms : 34.963
Note: B-factor plot
The average atomic B-factor per residue is plotted as function of
the residue number.
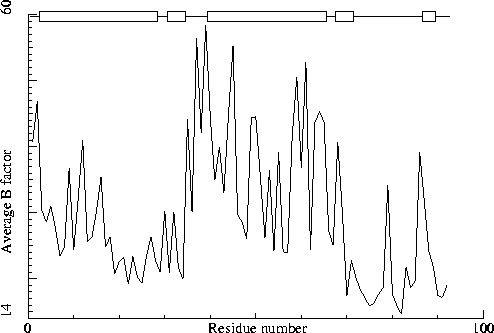
Chain without chain identifier
Hydrogen bond related checks
Note: HIS, ASN, GLN side chains OK
All of the side chain conformations of Histidine, Asparagine and
Glutamine residues were found to be optimal for hydrogen bonding.
Note: Histidine type assignments
For all complete HIS residues in the structure a tentative
assignment to HIS-D (protonated on ND1), HIS-E (protonated on NE2),
or HIS-H (protonated on both ND1 and NE2, positively charged) is
made based on the hydrogen bond network. A second assignment is
made based on which of the Engh and Huber [REF] histidine
geometries fits best to the structure.
In the table below all normal histidine residues are listed. The assignment based on the geometry of the residue is listed first, together with the RMS Z-score for the fit to the Engh and Huber parameters. For all residues where the H-bond assignment is different, the assignment is listed in the last columns, together with its RMS Z-score to the Engh and Huber parameters.
As always, the RMS Z-scores should be close to 1.0 if the residues were restrained to the Engh and Huber parameters during refinement.
Please note that because the differences between the geometries of the different types are small it is possible that the geometric assignment given here does not correspond to the type used in refinement. This is especially true if the RMS Z-scores are much higher than 1.0.
If the two assignments differ, or the ``geometry'' RMS Z-score is high, it is advisable to verify the hydrogen bond assignment, check the HIS type used during the refinement and possibly adjust it.
4 HIS ( 28 ) HIS-E 0.76 HIS-D 0.84 82 HIS ( 112 ) HIS-E 0.82
Hydrogen bond donors that are buried inside the protein normally use all of their hydrogens to form hydrogen bonds within the protein. If there are any non hydrogen bonded buried hydrogen bond donors in the structure they will be listed here. In very good structures the number of listed atoms will tend to zero.
85 ARG ( 115 ) N
The second part of the table mostly gives an impression of how well the model conforms to common refinement constraint values. The first part of the table shows a number of constraint-independent quality indicators.
Structure Z-scores, positive is better than average:
1st generation packing quality : -0.157 2nd generation packing quality : 2.592 Ramachandran plot appearance : -2.268 chi-1/chi-2 rotamer normality : 0.610 Backbone conformation : 1.501
Bond lengths : 0.711 Bond angles : 0.910 Omega angle restraints : 0.484 (tight) Side chain planarity : 0.076 (tight) Improper dihedral distribution : 0.661 Inside/Outside distribution : 1.217 (unusual)