Improper dihedral RMS Z-score : 0.518
Note: Chain names are OK
All chain names assigned to polymer molecules are unique, and all
residue numbers are strictly increasing within each chain.
Note: Weights checked OK
All atomic occupancy factors ('weights') fall in the 0.0--1.0 range.
Geometric checks
Note: No missing atoms detected
All expected atoms are present.
Warning: C-terminal oxygen atoms missing
The C-atoms listed in the table below belong to a C-terminal residue
in a protein chain, but the C-terminal oxygen ("O2" or "OXT") that it
should be bound to was not found.
408 MET ( 423 ) C
RMS Z-score for bond lengths: 0.758
RMS-deviation in bond distances: 0.017
Note: No bond length directionality
Comparison of bond distances with Engh and Huber [REF] standard
values for protein residues and Parkinson et al [REF] values for
DNA/RNA does not show significant systematic deviations.
Note: All bond angles OK
All bond angles are in agreement with standard bond angles using a
tolerance of 4 sigma (both standard values and sigma for protein
residues have been taken from Engh and Huber [REF], for DNA/RNA
from Parkinson et al. [REF]). Please note that only bond angles
within protein residues are taken into account: disulphide bridges
and peptide bonds are neglected.
Note: Normal bond angle variability
Bond angles were found to deviate normally from the mean standard
bond angles (normal values for protein residues were taken from
Engh and Huber [REF], for DNA/RNA from Parkinson et al [REF]). The
RMS Z-score given below is expected to be around 1.0 for a normally
restrained data set, and this is indeed observed for very high
resolution X-ray structures. More common values are around 1.55
RMS Z-score for bond angles: 0.895
RMS-deviation in bond angles: 1.776
Note: Side chain planarity OK
All of the side chains of residues that have a planar group are
planar within expected RMS deviations.
Note: Atoms connected to aromatic rings OK
All of the atoms that are connected to planar aromatic rings in side
chains of amino-acid residues are in the plane within expected RMS
deviations.
Warning: Unusual PRO puckering amplitudes
The proline residues listed in the table below have a puckering
amplitude that is outside of normal ranges. Puckering parameters
were calculated by the method of Cremer and Pople [REF]. Normal PRO
rings have a puckering amplitude Q between 0.20 and 0.45
Angstrom. If Q is lower than 0.20 Angstrom for a PRO residue, this
could indicate disorder between the two different normal ring forms
(with C-gamma below and above the ring, respectively). If Q is
higher than 0.45 Angstrom something could have gone wrong during the
refinement.
184 PRO ( 192 ) 0.14 LOW 188 PRO ( 196 ) 0.10 LOW
22 PRO ( 24 ) 47.4 half-chair C-delta/C-gamma (54 degrees) 336 PRO ( 348 ) 103.0 envelop C-beta (108 degrees)
These scores give an impression of how ``normal'' the torsion angles in protein residues are. All torsion angles except omega are used for calculating a `normality' score. Average values and standard deviations were obtained from the residues in the WHAT IF database. These are used to calculate Z-scores. A residue with a Z-score of below -2.0 is poor, and a score of less than -3.0 is worrying. For such residues more than one torsion angle is in a highly unlikely position.
351 THR ( 363 ) -2.8118 336 PRO ( 348 ) -2.8040 335 PHE ( 347 ) -2.4627 19 PHE ( 21 ) -2.4174 227 THR ( 237 ) -2.3671 378 MET ( 392 ) -2.2233 113 VAL ( 119 ) -2.1872 140 ASP ( 147 ) -2.1660 266 ARG ( 276 ) -2.1063 379 CYS ( 393 ) -2.0761 143 GLU ( 150 ) -2.0612 371 VAL ( 385 ) -2.0320 339 GLY ( 351 ) -2.0213
Residues with ``forbidden'' phi-psi combinations are listed, as well as residues with unusual omega angles (deviating by more than 3 sigma from the normal value). Please note that it is normal if about 5 percent of the residues is listed here as having unusual phi-psi combinations.
10 ASP ( 10 ) Poor phi/psi 20 LYS ( 22 ) Poor phi/psi 22 PRO ( 24 ) Poor PRO-phi 60 PRO ( 64 ) Poor PRO-phi 61 VAL ( 65 ) Poor phi/psi 121 TRP ( 127 ) Poor phi/psi 151 ALA ( 158 ) Poor phi/psi 154 ARG ( 161 ) Poor phi/psi 200 ALA ( 208 ) Poor phi/psi 202 LEU ( 210 ) omega poor 218 GLU ( 226 ) Poor phi/psi 220 SER ( 228 ) Poor phi/psi 221 ASP ( 229 ) Poor phi/psi 238 ASP ( 248 ) Poor phi/psi 246 LEU ( 256 ) PRO omega poor 247 PRO ( 257 ) Poor PRO-phi 265 GLY ( 275 ) Poor phi/psi 266 ARG ( 276 ) Poor phi/psi 269 ARG ( 279 ) Poor phi/psi 270 GLY ( 280 ) Poor phi/psi 336 PRO ( 348 ) Poor PRO-phi 337 GLY ( 349 ) Poor phi/psi 344 LEU ( 356 ) Poor phi/psi 351 THR ( 363 ) Poor phi/psi 366 ASP ( 380 ) Poor phi/psi 378 MET ( 392 ) omega poor
Ramachandran Z-score : -1.697
Warning: Omega angles too tightly restrained
The omega angles for trans-peptide bonds in a structure are
expected to give a gaussian distribution with the average around
+178 degrees and a standard deviation around 5.5 degrees. These
expected values were obtained from very accurately determined
structures. Many protein structures are too tightly constrained.
This seems to be the case with the current structure, as the
observed standard deviation is below 4.0 degrees.
Standard deviation of omega values : 3.441
Note: chi-1/chi-2 angle correlation Z-score OK
The score expressing how well the chi-1/chi-2 angles of all residues
are corresponding to the populated areas in the database is
within expected ranges for well-refined structures.
chi-1/chi-2 correlation Z-score : -0.903
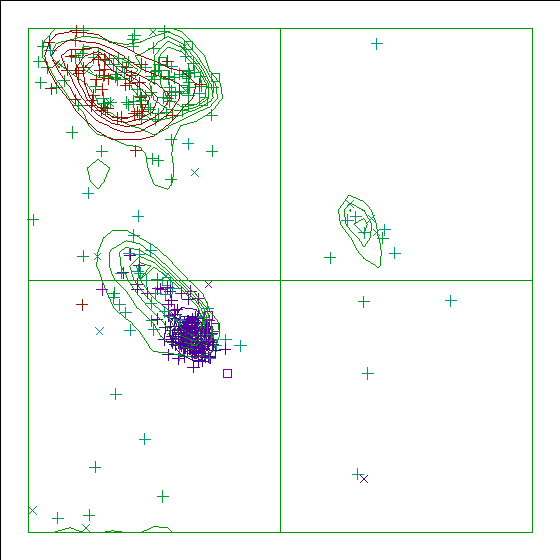
Note: Ramachandran plot
In this Ramachandran plot X-signs represent glycines, squares represent
prolines and small plus-signs represent the other residues. If too many
plus-signs fall outside the contoured areas then the molecule is poorly
refined (or worse).
In a colour picture, the residues that are part of a helix are shown in blue, strand residues in red. "Allowed" regions for helical residues are drawn in blue, for strand residues in red, and for all other residues in green.

Chain without chain identifier
Accessibility related checks
Note: Inside/Outside residue distribution normal
The distribution of residue types over the inside and the outside of the
protein is normal.
inside/outside RMS Z-score : 1.095
Note: Inside/Outside RMS Z-score plot
The Inside/Outside distribution normality RMS Z-score over a 15
residue window is plotted as function of the residue number. High
areas in the plot (above 1.5) indicate unusual inside/outside
patterns.
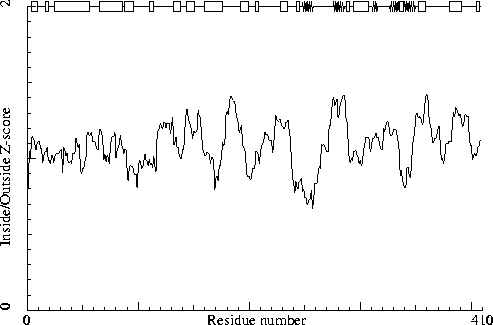
Chain without chain identifier
Secondary structure
Note: Secondary structure
This is the secondary structure according to DSSP. Only helix (H), strand
(S), turn (T) and coil (blank) are shown. [REF]
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
DBG> SSBOND cards to be written: 0
10
|
1 - 13 VLDLDLFRVDKGG
1 - 13 HHHHHH T
20 30 40 50
| | | |
14 - 57 TQEKRFKDPGLVDQLVKADSEWRRCRFRADNLSKLKNLCSKTIG
14 - 57 TT333T HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
60 70 80
| | |
58 - 86 KEPVGDDESVPENVLSFDDLTADALANLK
58 - 86 TT THHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
90 100 110 120 130
| | | | |
87 - 130 EAERFENLREIGNLLHPSVPISNDEDVDNKVERIWGDCTVRKKY
87 - 130 HHHHHHHHT TTT TT333 T TT
140 150 160 170
| | | |
131 - 176 SHVDLVVMVDGFEGEKGAVVAGSRGYFLKGVLVFLEQALIQYALRT
131 - 176 HHHHHHHTT HHHHHHHT TT HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHH
180 190 200 210 220
| | | | |
177 - 223 LGSRGYIPIYTPFFMRKEVMQEVAQLSQFDEELYKVIGKGSEKSDDN
177 - 223 TT T HHHHHHHT TTTT333T TT
230 240 250 260 270 280
| | | | | |
224 - 283 LIATSEQPIAALHRDEWLRPEDLPIKYAGLSTCFRQEVGSHGRDTRGIFRVHQFEKIEQF
224 - 283 T THHHHHHTTTT 333 SSSSSSSSSS T TT T TSSSSSSSS
290
|
284 - 292 VYSSPHDNK
284 - 292 SS 333
300 310 320 330 340 350
| | | | | |
293 - 352 FEEMITTAEEFYQSLGIPYHIVNIVSGSLNHAASKKLDLEAWFPGSGAFRELVSCSNCTD
293 - 352 HHHHHHHHHHHHHHT SSSSS TTTT TT TSSSSSSSSS333TSSSSSSSSSS TT
360
|
353 - 363 YQARRLRIRYG
353 - 363 HHHHHHT
370 380 390
| | |
364 - 397 MMDKVEFVHMLNATMCATTRTICAILENYQTEKG
364 - 397 T HHHHHHHHHHHT TT
400
|
398 - 408 ITVPEKLKEFM
398 - 408 TTT333
The contact distances of all atom pairs have been checked. Two atoms are said to `bump' if they are closer than the sum of their Van der Waals radii minus 0.40 Angstrom. For hydrogen bonded pairs a tolerance of 0.55 Angstrom is used. The first number in the table tells you how much shorter that specific contact is than the acceptable limit. The second distance is the distance between the centers of the two atoms.
The last text-item on each line represents the status of the atom pair. The text `INTRA' means that the bump is between atoms that are explicitly listed in the PDB file. `INTER' means it is an inter-symmetry bump. If the final column contains the text 'HB', the bump criterium was relaxed because there could be a hydrogen bond. Similarly relaxed criteria are used for 1--3 and 1--4 interactions (listed as 'B2' and 'B3', respectively). If the last column is 'BF', the sum of the B-factors of the atoms is higher than 80, which makes the appearance of the bump somewhat less severe because the atoms probably aren't there anyway.
Bumps between atoms for which the sum of their occupancies is lower than one are not reported. In any case, each bump is listed in only one direction.
64 ASP ( 68 ) O -- 68 PRO ( 72 ) CD 1.305 1.495 INTRA 243 PRO ( 253 ) CD -- 363 GLY ( 375 ) O 1.078 1.722 INTRA 171 GLN ( 178 ) CB -- 407 PHE ( 422 ) CE2 1.054 2.146 INTRA 171 GLN ( 178 ) CG -- 407 PHE ( 422 ) CE2 1.003 2.197 INTRA 347 CYS ( 359 ) SG -- 376 ALA ( 390 ) CB 0.895 2.505 INTRA 64 ASP ( 68 ) C -- 68 PRO ( 72 ) CD 0.625 2.575 INTRA 108 SER ( 114 ) CB -- 317 VAL ( 329 ) CB 0.568 2.632 INTRA 199 VAL ( 207 ) O -- 200 ALA ( 208 ) CB 0.561 2.239 INTRA 228 SER ( 238 ) OG -- 281 GLU ( 291 ) CB 0.560 2.240 INTRA 108 SER ( 114 ) CB -- 317 VAL ( 329 ) CG1 0.494 2.706 INTRA 108 SER ( 114 ) CB -- 113 VAL ( 119 ) CB 0.487 2.713 INTRA 7 PHE ( 7 ) CZ -- 97 ILE ( 103 ) CD1 0.485 2.715 INTRA 243 PRO ( 253 ) CG -- 363 GLY ( 375 ) O 0.474 2.326 INTRA 171 GLN ( 178 ) CB -- 407 PHE ( 422 ) CD2 0.470 2.730 INTRA 59 GLU ( 63 ) N -- 60 PRO ( 64 ) CD 0.452 2.548 INTRA 113 VAL ( 119 ) O -- 317 VAL ( 329 ) CG1 0.419 2.381 INTRA 198 GLU ( 206 ) CB -- 358 LEU ( 370 ) CG 0.414 2.786 INTRA 19 PHE ( 21 ) CE1 -- 101 LEU ( 107 ) CB 0.403 2.797 INTRA 203 SER ( 211 ) O -- 206 ASP ( 214 ) OD1 0.388 2.012 INTRA 344 LEU ( 356 ) CD2 -- 383 ARG ( 397 ) CB 0.377 2.823 INTRA 293 PHE ( 305 ) CE1 -- 347 CYS ( 359 ) O 0.377 2.423 INTRA 347 CYS ( 359 ) CB -- 376 ALA ( 390 ) CB 0.363 2.837 INTRA 19 PHE ( 21 ) CE1 -- 318 SER ( 330 ) CA 0.361 2.839 INTRA 171 GLN ( 178 ) CG -- 407 PHE ( 422 ) CZ 0.355 2.845 INTRA 296 MET ( 308 ) CE -- 374 LEU ( 388 ) CB 0.348 2.852 INTRAAnd so on for a total of 249 lines
The packing environment of the residues is compared with the average packing environment for all residues of the same type in good PDB files. A low packing score can indicate one of several things: Poor packing, misthreading of the sequence through the density, crystal contacts, contacts with a co-factor, or the residue is part of the active site. It is not uncommon to see a few of these, but in any case this requires further inspection of the residue.
186 TYR ( 194 ) -8.31 127 ARG ( 133 ) -7.73 269 ARG ( 279 ) -7.50 129 LYS ( 135 ) -6.63 215 LYS ( 223 ) -6.55 396 LYS ( 410 ) -6.40 365 MET ( 379 ) -6.05 219 LYS ( 227 ) -5.68 266 ARG ( 276 ) -5.50 180 ARG ( 188 ) -5.43 273 ARG ( 283 ) -5.18 289 HIS ( 299 ) -5.12 190 PHE ( 198 ) -5.03
The table below lists the first and last residue in each stretch found, as well as the average residue score of the series.
18 ARG ( 20 ) --- 20 LYS ( 22 ) -4.44
Average for range 1 - 408 : -0.985
Note: Quality value plot
The quality value smoothed over a 10 residue window is plotted as
function of the residue number. Low areas in the plot (below
-2.0) indicate "unusual" packing.
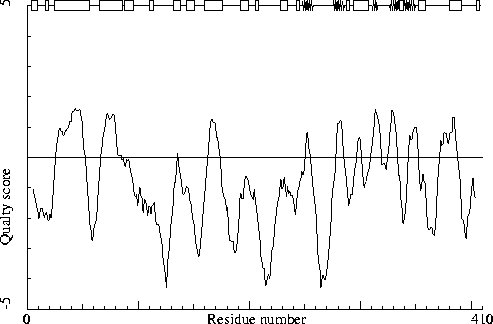
Chain without chain identifier
Warning: Low packing Z-score for some residues
The residues listed in the table below have an unusual packing
environment according to the 2nd generation quality check. The score
listed in the table is a packing normality Z-score: positive means
better than average, negative means worse than average. Only residues
scoring less than -2.50 are listed here. These are the "unusual"
residues in the structure, so it will be interesting to take a
special look at them.
289 HIS ( 299 ) -3.08 186 TYR ( 194 ) -2.78 213 ILE ( 221 ) -2.73 272 PHE ( 282 ) -2.56
The table below lists the first and last residue in each stretch found, as well as the average residue Z-score of the series.
123 ASP ( 129 ) --- 126 VAL ( 132 ) -2.33 269 ARG ( 279 ) --- 272 PHE ( 282 ) -2.31
All contacts : Average = -0.264 Z-score = -1.59
BB-BB contacts : Average = 0.077 Z-score = 0.56
BB-SC contacts : Average = -0.460 Z-score = -2.44
SC-BB contacts : Average = 0.026 Z-score = 0.33
SC-SC contacts : Average = -0.412 Z-score = -1.95
Note: Second generation quality Z-score plot
The second generation quality Z-score smoothed over a 10 residue window
is plotted as function of the residue number. Low areas in the plot (below
-1.3) indicate "unusual" packing.
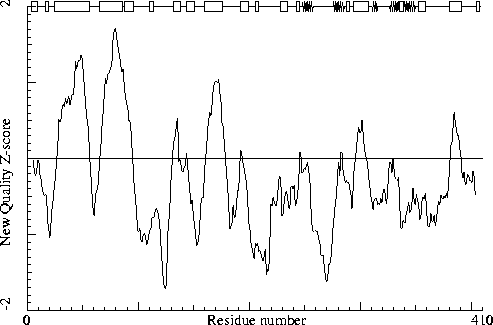
Chain without chain identifier
Note: Backbone oxygen evaluation OK
All residues for which the local backbone conformation could be
found in the WHAT IF database have a normal backbone oxygen
position.
Warning: Unusual rotamers
The residues listed in the table below have a rotamer that is not
seen very often in the database of solved protein structures. This
option determines for every residue the position specific chi-1
rotamer distribution. Thereafter it verified whether the actual
residue in the molecule has the most preferred rotamer or not. If
the actual rotamer is the preferred one, the score is 1.0. If the
actual rotamer is unique, the score is 0.0. If there are two
preferred rotamers, with a population distribution of 3:2 and your
rotamer sits in the lesser populated rotamer, the score will be
0.66. No value will be given if insufficient hits are found in the
database.
It is not necessarily an error if a few residues have rotamer values below 0.3, but careful inspection of all residues with these low values could be worth it.
402 GLU ( 417 ) 0.33
For this check, backbone conformations are compared with database structures using C-alpha superpositions with some restraints on the backbone oxygen positions.
A residue mentioned in the table can be part of a strange loop, or there might be something wrong with it or its directly surrounding residues. There are a few of these in every protein, but in any case it is worth looking at!
60 PRO ( 64 ) 0 61 VAL ( 65 ) 0 121 TRP ( 127 ) 0 151 ALA ( 158 ) 0 200 ALA ( 208 ) 0 202 LEU ( 210 ) 0 266 ARG ( 276 ) 0 351 THR ( 363 ) 0 378 MET ( 392 ) 0 379 CYS ( 393 ) 0 159 LYS ( 166 ) 1 218 GLU ( 226 ) 1 246 LEU ( 256 ) 1 154 ARG ( 161 ) 2 161 VAL ( 168 ) 2 203 SER ( 211 ) 2 220 SER ( 228 ) 2 350 CYS ( 362 ) 2
Backbone conformation Z-score : -0.105
B-factor analysis
Note: Average B-factor OK
The average B-factor of buried atoms is within expected values for
a room-temperature X-ray study.
Average B-factor for buried atoms : 22.234
Note: Number of buried atoms with low B-factor is OK
For protein structures determined at room temperature, no more than
about 1 percent of the B factors of buried atoms is below 5.0.
Percentage of buried atoms with B less than 5 : 0.07
Error: The B-factors of bonded atoms show signs of over-refinement
For each of the bond types in a protein a distribution was derived
for the difference between the square roots of the B-factors of the
two atoms. All bonds in the current protein were scored against
these distributions. The number given below is the RMS Z-score over
the structure. For a structure with completely restrained B-factors
within residues, this value will be around 0.35, for extremely high
resolution structures refined with free isotropic B-factors this
number is expected to be near 1.0. Any value over 1.5 is sign of
severe over-refinement of B-factors.
RMS Z-score : 2.100 over 2790 bonds
Average difference in B over a bond : 2.44
RMS difference in B over a bond : 6.24
Note: B-factor plot
The average atomic B-factor per residue is plotted as function of
the residue number.
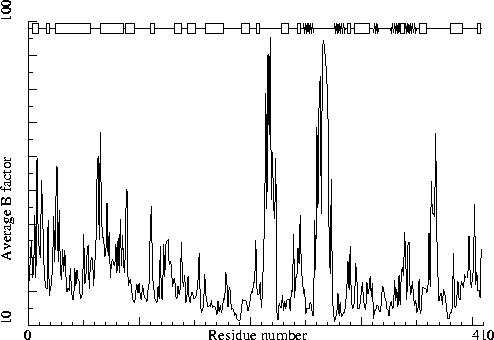
Chain without chain identifier
Hydrogen bond related checks
Error: HIS, ASN, GLN side chain flips
Listed here are Histidine, Asparagine or Glutamine residues for
which the orientation determined from hydrogen bonding analysis are
different from the assignment given in the input. Either they could
form energetically more favorable hydrogen bonds if the terminal
group was rotated by 180 degrees, or there is no assignment in the
input file (atom type 'A') but an assignment could be made. If a
residue is marked ``flexible'' the flipped conformation is only
slightly better than the non-flipped conformation.
264 HIS ( 274 ) 282 GLN ( 292 ) 291 ASN ( 301 ) 315 ASN ( 327 ) 349 ASN ( 361 )
In the table below all normal histidine residues are listed. The assignment based on the geometry of the residue is listed first, together with the RMS Z-score for the fit to the Engh and Huber parameters. For all residues where the H-bond assignment is different, the assignment is listed in the last columns, together with its RMS Z-score to the Engh and Huber parameters.
As always, the RMS Z-scores should be close to 1.0 if the residues were restrained to the Engh and Huber parameters during refinement.
Please note that because the differences between the geometries of the different types are small it is possible that the geometric assignment given here does not correspond to the type used in refinement. This is especially true if the RMS Z-scores are much higher than 1.0.
If the two assignments differ, or the ``geometry'' RMS Z-score is high, it is advisable to verify the hydrogen bond assignment, check the HIS type used during the refinement and possibly adjust it.
102 HIS ( 108 ) HIS-E 0.76 132 HIS ( 139 ) HIS-E 0.73 HIS-D 0.88 236 HIS ( 246 ) HIS-D 0.75 264 HIS ( 274 ) HIS-E 0.77 275 HIS ( 285 ) HIS-D 0.80 289 HIS ( 299 ) HIS-E 0.75 312 HIS ( 324 ) HIS-D 0.74 HIS-E 0.87 323 HIS ( 335 ) HIS-D 0.77 HIS-E 0.90 372 HIS ( 386 ) HIS-E 0.78 HIS-D 1.01
Hydrogen bond donors that are buried inside the protein normally use all of their hydrogens to form hydrogen bonds within the protein. If there are any non hydrogen bonded buried hydrogen bond donors in the structure they will be listed here. In very good structures the number of listed atoms will tend to zero.
1 VAL ( 1 ) N 2 LEU ( 2 ) N 15 GLN ( 17 ) N 18 ARG ( 20 ) NE 59 GLU ( 63 ) N 62 GLY ( 66 ) N 90 ARG ( 96 ) N 95 ARG ( 101 ) NE 109 ASN ( 115 ) N 124 CYS ( 130 ) N 133 VAL ( 140 ) N 134 ASP ( 141 ) N 146 LYS ( 153 ) N 180 ARG ( 188 ) N 180 ARG ( 188 ) NE 180 ARG ( 188 ) NH2 182 TYR ( 190 ) N 190 PHE ( 198 ) N 201 GLN ( 209 ) NE2 203 SER ( 211 ) OG 204 GLN ( 212 ) N 210 TYR ( 218 ) N 226 ALA ( 236 ) N 227 THR ( 237 ) N 228 SER ( 238 ) N 244 GLU ( 254 ) N 269 ARG ( 279 ) NH2 270 GLY ( 280 ) N 304 TYR ( 316 ) OH 315 ASN ( 327 ) ND2 322 ASN ( 334 ) N 327 LYS ( 339 ) N 328 LYS ( 340 ) N 340 ALA ( 352 ) N 352 ASP ( 364 ) N 354 GLN ( 366 ) N 355 ALA ( 367 ) N 381 THR ( 395 ) OG1 383 ARG ( 397 ) N 393 GLN ( 407 ) N 394 THR ( 408 ) N 403 LYS ( 418 ) N
Side-chain hydrogen bond acceptors that are buried inside the protein normally form hydrogen bonds within the protein. If there are any not hydrogen bonded in the optimized hydrogen bond network they will be listed here.
198 GLU ( 206 ) OE1 312 HIS ( 324 ) ND1 354 GLN ( 366 ) OE1 391 ASN ( 405 ) OD1
The second part of the table mostly gives an impression of how well the model conforms to common refinement constraint values. The first part of the table shows a number of constraint-independent quality indicators.
Structure Z-scores, positive is better than average:
1st generation packing quality : -1.213 2nd generation packing quality : -1.593 Ramachandran plot appearance : -1.697 chi-1/chi-2 rotamer normality : -0.903 Backbone conformation : -0.105
Bond lengths : 0.758 Bond angles : 0.895 Omega angle restraints : 0.626 (tight) Side chain planarity : 0.076 (tight) Improper dihedral distribution : 0.518 B-factor distribution : 2.100 (loose) Inside/Outside distribution : 1.095