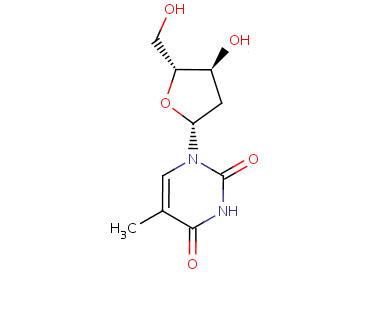
Figure 52. The THM molecule. (Actually, almost the THM molecule, there is a small error in this plot (sorry). The coordinates you get to see in YASARA are correct, this picture is a tiny bit wrong).
First, we have a look at the starting complex. This is a protein called thymidine kinase bound to a molecule called deoxythymidine (THM). The THM molecule is drawn below:

|
Figure 52. The THM molecule. (Actually, almost the THM molecule, there is a small error in this plot (sorry). The coordinates you get to see in YASARA are correct, this picture is a tiny bit wrong). |
The PDB code of the thymidine kinase-THM complex is 1kim. Load the file 1kim.sce from the exercise section and read it in YASARA with the Load YASARA scene option (File > Load > Yasara Scene). The amino acids in the binding pocket are coloured light-blue, the ligand is coloured orange.
Question 67: You see the binding pocket of thymidine kinase with thymidine bound. Write down the residue names and numbers of the amino acids in the protein to which the ligand makes hydrogen bonds.
AnswerWe now want to dock a newly designed molecule into this 'thymidine kinase' structure using Fleksy. The newly designed molecule (named BTD) looks like this:
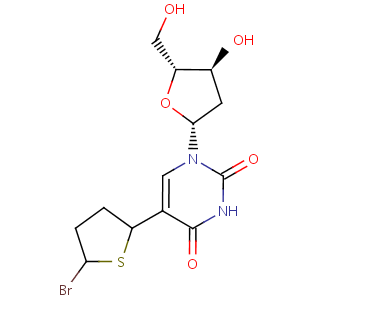
|
Figure 53. The BTD molecule. |
Question 68: What is the main difference between the original molecule THM and the newly designed molecule BTD?
Answer
Question 69: Look again at the THM molecule bound in 1kim.sce. In the direction of which amino acids do you expect the newly introduced group to point?
Answer
Question 70: Do you think there is enough space in the binding pocket shown for THM to accommodate the BTD molecule? Do you expect any clashes to occur?
(Hint: Ask the assistant how to measure distances in YASARA, and how to guess them from a 2D plot of a molecule).
AnswerWe tried to perform a rigid receptor docking of the BTD molecule into the binding pocket of the 1kim structure. The docking program failed to produce any solutions.
Question 71: What does this tell you about the answer you wrote down for the previous question?
AnswerOur next attempt at docking this molecule is to try to use Fleksy to model the protein flexibility required to dock the BTD molecule.
Question 72: For this docking experiment you get to select one (1!) amino acid in the protein to make it flexible during the docking. Which one would you choose? Explain why!
AnswerYou can find the result of our Fleksy docking in the file fleksy.sce. Download the file fleksy.sce and open it using Yasara (File > Load > Yasara Scene). This scene contains two objects (you can see that in the top right corner of your screen).
Object 1 is the structure of thymidine kinase bound to THM (pdb entry 1kim), as you saw before. Object 2 is the prediction Fleksy made for the BTD molecule. You can switch between the two object by clicking in the 'Vis' column next to the object name in the top right corner of your screen.
Question 73: Look at the predicted binding mode for the BTD molecule made by Fleksy. With which amino acids does the new group make contacts? Does the new group in BTD go where you expected it to go?
Answer
Question 74: Which amino acid in the Fleksy result has moved the most compared to the original 1kim structure? In other words: which amino acids was made flexible during the docking?
Answer
Question 75: For the Fleksy result, write down the residue names and numbers of the amino acids in the protein to which BTD makes hydrogen bonds. Are the hydrogen bonds you wrote down in the first docking question all retained?
Answer
Question 76: Do you think Fleksy did a good job? Why or why not?
Answer